- Trading
Trading
-
CFD Trading
What is CFD Trading How to Trade CFD Why Trade CFD CFD Trading Strategies
- All Trading Products
-
Markets
All Instruments Forex CFDs Indices CFD Commodities CFD Stocks CFD ETFs CFD Bonds CFD Cryptocurrency CFDs
- Trading Accounts
- Trading Fees
- Trading Leverage
- Trading Server
- Deposit & Withdrawal
- Premium Services
-
CFD Trading
- Platforms
- Academy
- Analysis
- About
-
AllTradingPlatformsAcademyAnalysisAbout
-
Search query too short. Please enter a full word or phrase.
-
Keywords
- Trading Accounts
- TradingView
- Trading Fees
Popular Search
- Trading Accounts
- MT4
- MT5
- Professional Trading Accounts
- Academy
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is the global marketplace for buying and selling currencies. In this guide, we will walk you through the essentials of forex trading, how it works, and the key concepts every forex trader should understand.
What Is Forex (FX) Trading?
At its core, Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another, with the goal of profiting from price fluctuations. Unlike stock markets, which operate within centralised exchanges, forex trading takes place over-the-counter (OTC), meaning it is conducted electronically through a global network of banks, financial institutions, governments, and individual traders. Governments participate to manage their currency reserves and influence monetary policy, while banks play a central role in facilitating transactions and providing liquidity.
Due to its high liquidity, forex is the most actively traded market in the world. It allows businesses to facilitate international trade, investors to hedge against currency fluctuations, and traders to speculate on price movements for potential profit. Additionally, central banks and governments intervene in the forex market to stabilise or devalue their currencies, impacting global exchange rates.
How Forex Trading Works
Forex trading operates through a decentralised market where participants, including banks, financial institutions, and retail traders, exchange currencies. Prices fluctuate based on supply and demand, geopolitical events, and economic data.
For example, if you expect the GBP/USD exchange rate to rise, you could buy GBP against USD and sell when the price increases to make a profit. You decide to buy GBP/USD at an exchange rate of 1.3000. If the rate rises to 1.3100, you can sell your GBP for a profit. However, if it drops to 1.2900, you will incur a loss.
When trading forex with a brokerage, be aware of costs, such as spreads, commissions, and overnight financing fees. These fees can significantly impact your profitability. Trading also involves the risk of losing your invested capital.
How Currency Pairs Work
Currencies are always traded in pairs, where one currency is bought while the other is sold. The first currency in the pair is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency.
Here’s how you can read the EUR/USD currency pair:
The first currency is known as the base currency which is the Euro (EUR).
The second currency is known as the quote currency which is the US dollar (USD).
The exchange rate shows how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
Major Currency Pairs (or Majors)
Major currency pairs include the most traded currencies globally, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY and USD/CHF. These pairs typically have high liquidity and lower spreads, making them popular among traders.
Four Majors
| Pair | Name | Nickname |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | Euro Dollar | Fiber |
| USD/JPY | Dollar Yen | Gopher |
| GBP/USD | Pound Dollar | Cable |
| USD/CHF | Dollar Swiss | Swissie |
Minor and Exotic Currency Pairs
Minor currency pairs exclude the US dollar, such as EUR/GBP or AUD/JPY. Exotic pairs involve a major currency paired with an emerging market currency, such as USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR. These pairs often have wider spreads and higher volatility.
| Pair | Name |
|---|---|
| EUR/GBP | Euro Pound |
| GBP/JPY | Pound Yen |
| EUR/AUD | Euro |
| GBP/CAD | Pound |
| EUR/CHF | Euro Swiss |
Understanding Key Concepts and Terms About Forex Trading
To trade forex effectively, it is essential to grasp fundamental concepts such as spreads, pips, leverage, margin, and lot sizes. Understanding these terms may help you make informed trading decisions.
What Are Spreads and Pips in Forex?
Spreads and pips are essential to understanding trading costs and price movements in forex. They determine how prices fluctuate and directly impact your trading profitability.
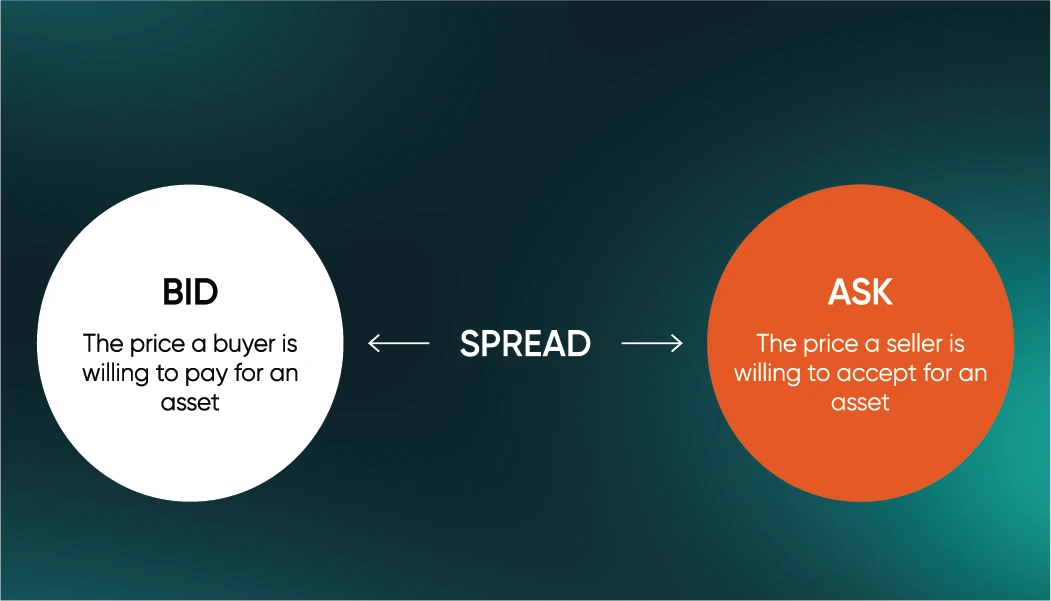
What are spreads
The spread is the difference between the bid (selling) price and the ask (buying) price of a currency pair. This is essentially the cost of trading, and it varies depending on market conditions and liquidity. Brokers may offer either fixed or variable spreads.
What are pips?
A pip, short for "percentage in point," is the smallest price movement in forex trading. It is usually the fourth decimal place in a currency quote (except for JPY pairs, where it is the second decimal place). For example, if EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1005, the price has increased by 5 pips.
Leverage and Margin Explained
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, while margin is the capital required to open and maintain a leveraged position.
What is Leverage
Leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 10:1, 20:1, or 30:1, indicating how much a trader can control relative to their invested capital. For instance, with 30:1 leverage, a trader can control a $9,000 position with only $300 in their account. Leverage magnifies both potential profits and potential losses. It can lead to rapid losses, potentially exceeding your initial deposit. You should only use leverage if you fully understand the risks involved.
What is Margin?
Margin is the portion of capital required to open a leveraged trade. If market movements push the trader's losses beyond a certain level, the broker may issue a margin call, requiring additional funds or leading to trade liquidation to prevent further losses.
How Leverage and Margin Work in Forex
Imagine you have $1,000 in your trading account and use 30:1 leverage to open a $30,000 position on EUR/USD at an exchange rate of 1.1000.
If the price rises to 1.1050 (a 50-pip increase), your profit would be around $150, assuming a standard lot size (30,000 units).
Profit = (New price – Entry Price) x Position Size
Profit = (1.1050 - 1.1000) x 30,000 = 0.0050 x 30,000 = $150
However, if the price drops to 1.0950 (a 50-pip decline), you would face a $150 loss.
Loss = (Entry Price - New Price) × Position Size
Loss = (1.1000 - 1.0950) × 30,000 = 0.0050 × 30,000 = $150
If the market moves further against you without a stop-loss in place, your losses could exceed your $1,000 deposit, leading to a margin call from your broker.
This highlights the importance of using risk management tools like stop-loss orders to protect your capital.
What Are Lots in Forex Trading?
A lot represents a standardised contract size in forex trading. The lot size you choose impacts your risk exposure and potential profits or losses.
- Standard lot:100,000 units of currency
- Mini lot:10,000 units
- Micro lot:1,000 units
- Nano lot:100 units
Lot size affects risk exposure. For example, a trader with a smaller capital base may prefer micro or mini lots to manage risk.
What Moves the Forex Market?
The forex market is the most liquid market in the world for several reasons. There are multiple factors that drive forex price movements, including:
Economic indicators
Economic indicators provide insight into a country’s financial health and can significantly impact currency prices. Data such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment reports, inflation rates, and consumer spending figures influence market expectations. For example, if a country’s GDP growth surpasses forecasts, its currency may strengthen due to increased investor confidence.
Central bank policies
Monetary policies set by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank, play a critical role in forex market fluctuations. Interest rate decisions, quantitative easing, and direct currency interventions can all drive currency values. A higher interest rate generally attracts foreign capital, boosting the currency’s value, while lower rates can weaken it.
Geopolitical events
Political stability, trade agreements, and global crises all impact forex markets. Elections, economic sanctions, or diplomatic conflicts can trigger fluctuations in currency pairs. For instance, uncertainty surrounding Brexit negotiations led to significant volatility in GBP-related pairs, affecting traders and investors alike.
Market sentiment
Trader behaviour and overall market confidence influence currency movements. Risk appetite increases demand for higher-yielding currencies, while uncertainty can drive investors toward safe-haven assets like the US dollar or gold. Speculation, news sentiment, and investor psychology all contribute to market trends.
What Is a Forex Broker?
A forex broker acts as an intermediary, providing traders with access to the forex market via trading platforms. Brokers facilitate trades and offer leverage, margin accounts, and other trading tools. They typically make money through spreads, commissions, or overnight financing fees.
Discover the Risks and Rewards of Trading Forex
Like any financial market, forex trading comes with both opportunities and challenges that traders should carefully consider. Here are some potential rewards and risks that is associated with forex trading:
| Rewards | Risks |
|---|---|
| High liquidity allows for ease of entry and exit from positions | High Market volatility can lead to rapid and substantial losses. |
| Potential for profit in rising and falling markets | Leverage significantly increases your risk exposure. Small price movements can have a large impact on your account balance, both positive and negative. |
| Availability of leverage to maximise potential trading opportunities | Unpredictable economic, geopolitical, and regulatory factors can cause sudden and significant market movements, leading to losses. |
By understanding these fundamental aspects of forex trading, you can make informed decisions and develop a solid trading strategy.
Explore More About Forex Trading
-
How to trade forex
Discover step-by-step guidance on how to start trading Forex via CFDs, from opening an account to executing your first trade.
-
Why trade forex
Find out the unique benefits and advantages that trading forex can offer, and why any serious trader should consider this dynamic market.
-
Forex Trading Strategies
Explore Forex trading strategies via CFDs to help you navigate potential market opportunities while managing risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
1
What is forex trading?
Forex trading is the buying and selling of currencies to profit from exchange rate fluctuations. It’s the world’s largest financial market, operating 24/5, but it involves significant risk of loss. -
2
What is CFD in forex?
A CFD (Contract for Difference) allows traders to speculate on forex price movements without owning the currency. CFDs are complex instruments and offer leverage, which can magnify both profits and losses. CFDs carry a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. Ensure you understand the risks before trading CFDs. -
3
What’s the difference between Forex exchange trading and currency trading?
Forex trading focuses on speculating currency price movements for profit, while currency trading can also refer to money exchanges for travel, business, or global trade. -
4
What is the forex market?
The forex market is a global, decentralised marketplace where currencies are traded 24/5. It includes banks, financial institutions, and traders exchanging currencies based on fluctuating rates. -
5
What is a forex broker?
A forex broker is a financial intermediary that provides access to the forex market, offering trading platforms, leverage, and tools to execute trades. -
6
What does a forex broker do?
A forex broker facilitates currency trades, earns through spreads or commissions, and may provide trading tools, market insights, and risk management features.